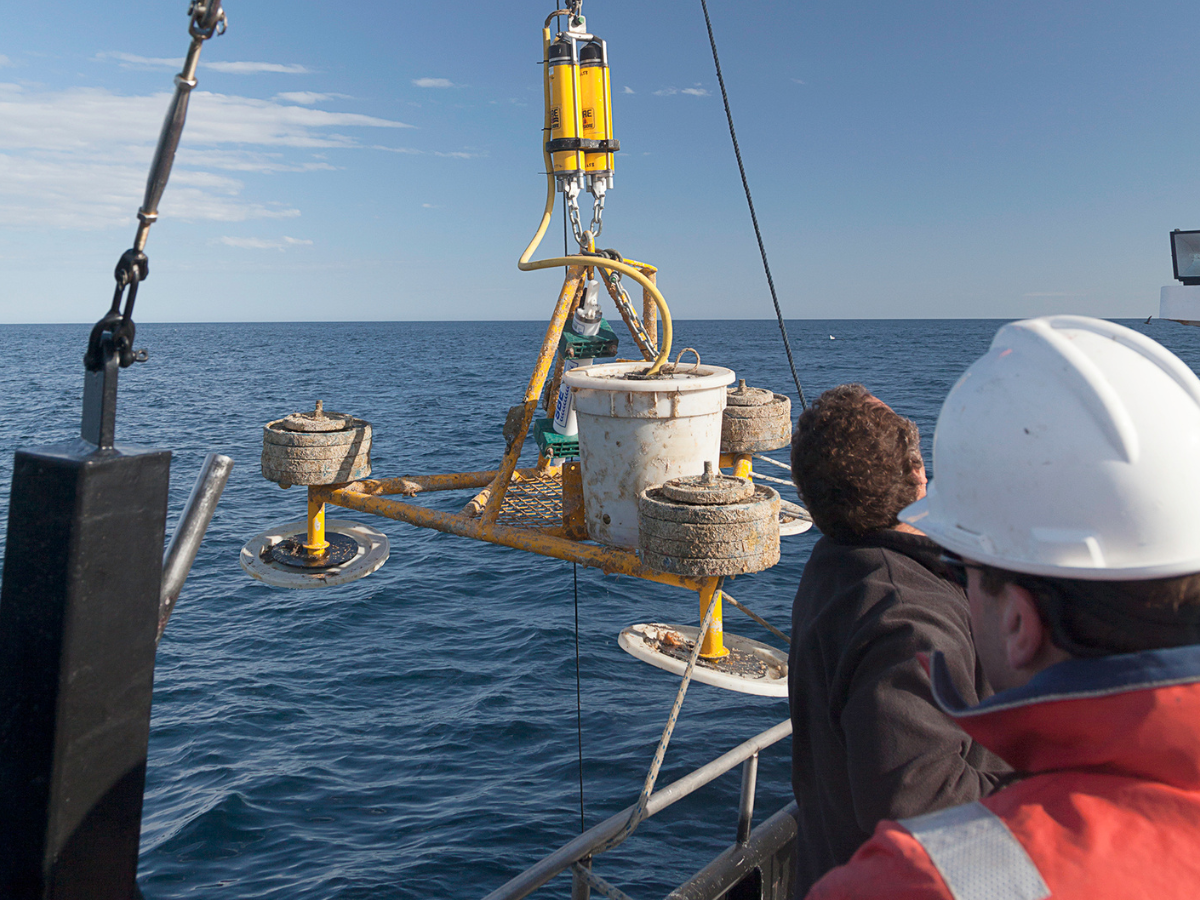
Deep Argo Floats
Deep Argo Floats
Argo Floats measure temperature, conductivity (for conversion to salinity), and pressure in the upper 2 km of the ocean. By providing continuous observations of the global ocean, Argo floats have revolutionised our understanding of the oceans and their role in climate.
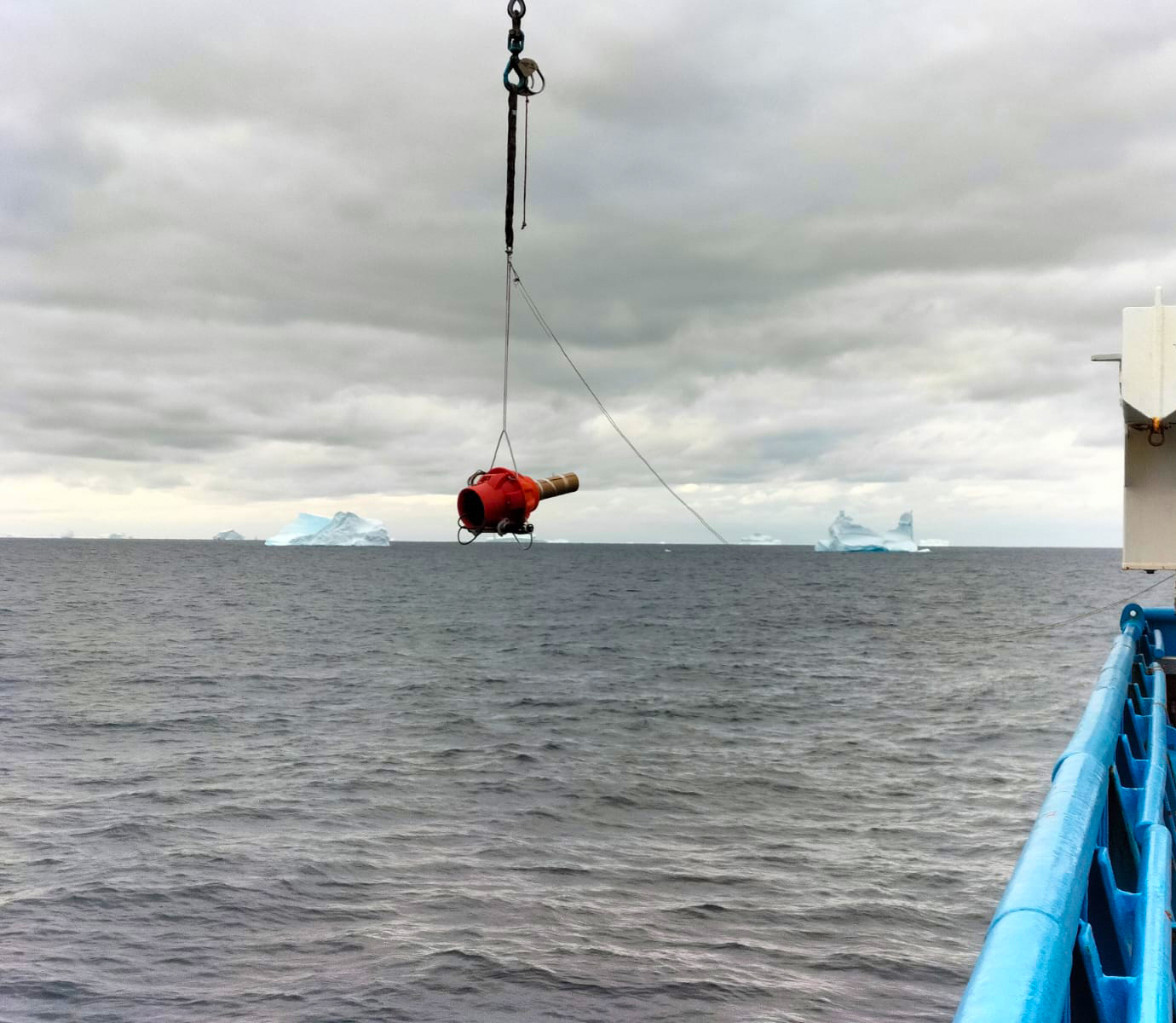

 AAPP, CSIRO
AAPP, CSIRO
Measurements
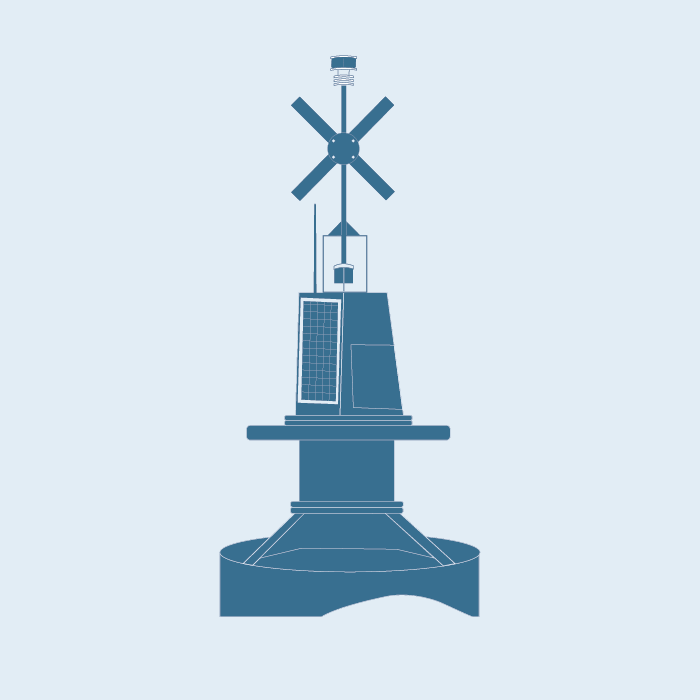
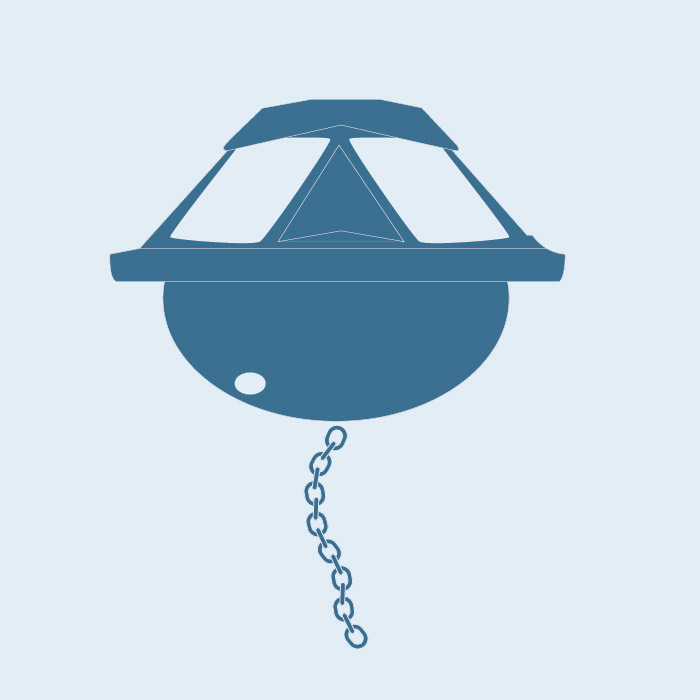
Regular Argo floats only sample about half the ocean volume. Sparse ship-based measurements show that change is also underway in the deep ocean. Recognising the urgent need for more complete sampling of the deeper part of the ocean, the International Argo community has developed Deep Argo Floats that can reliably measure temperature and salinity to depths of 6 km.
Why it’s important
The sustained, continuous measurements provided by Deep Argo Floats will allow changes in the deep ocean to be assessed and understood for the first time. Deep Argo will provide crucial measurements for tracking changes in ocean heat content, salinity, sea level rise, and deep circulation. The deep ocean slows the rate of climate change by taking up heat and carbon, therefore changes in the deep ocean may affect the pace of climate change.

Deep ocean revolution
The Deep Argo Floats sub-Facility will enhance Argo Australia by adding deep floats able to profile the full water depth, and contribute to the global array target of 1200 Deep Argo Floats. Just as Argo has revolutionised oceanography in the upper ocean, Deep Argo will drive a similar revolution in the deep ocean.
Key data streams
Select a key data stream to view all IMOS Facilities that collect that data.
Useful information
Acknowledging IMOS
Users of IMOS data are required to clearly acknowledge the source material by including the following statement:
Australia’s Integrated Marine Observing System (IMOS) is enabled by the National Collaborative Research Infrastructure Strategy (NCRIS). It is operated by a consortium of institutions as an unincorporated joint venture, with the University of Tasmania as Lead Agent.